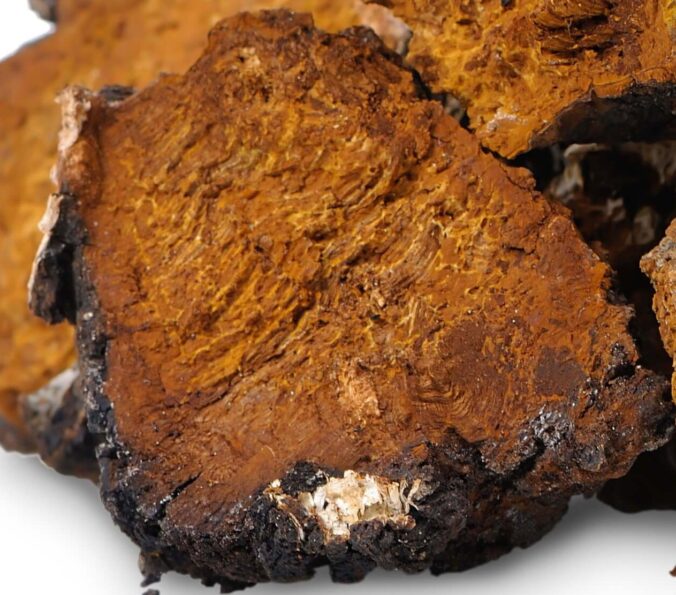
Chaga mushroom (Inonotus obliquus) is a powerful medicinal mushroom that has been used by indigenous people of South America for centuries to treat a variety of health conditions. This fungus is well-known for its ability to boost the immune system, improve digestion, and protect against chronic diseases such as cancer and autoimmune disorders. In this blog post, we will explore the history of chaga mushroom in natural medicine and dive into its active constituents and their mechanisms of action.
Chaga mushroom has a long history of use among indigenous people of South America. It was used by various tribes for a variety of health conditions, including arthritis, digestive issues, fever, and infections. The mushroom was also used as a tonic to improve overall health and well-being.
The active constituents in chaga mushroom are primarily found in its mycelium (the underground part of the fungus) and sclerotia (the hard, compact mass of tissue that forms in some fungi). The most notable active constituent is betulinic acid, which has been shown to have powerful immune-boosting properties, antioxidant effects, and anti-inflammatory effects.
Other active constituents found in chaga mushroom include polysaccharides such as beta-glucan, which work to stimulate the production of white blood cells and help combat infections. Additionally, chaga mushroom contains various minerals and vitamins, including copper, zinc, and manganese, which contribute to its overall health benefits. Chaga mushroom has been shown to work through several different mechanisms of action, which include: Immune-boosting effects: Betulinic acid stimulates the production of white blood cells and helps combat infections by disrupting the cell membranes of bacteria and other microorganisms. The polysaccharides such as beta-glucan also help to regulate the immune system and protect against autoimmune disorders.Antioxidant effects: Chaga mushroom contains powerful antioxidants that help combat free radicals in the body, which can cause oxidative stress and contribute to chronic diseases such as cancer and autoimmune disorders. Betulinic acid is also thought to play a role in inhibiting the growth of cancer cells by inducing apoptosis (cell death) in these cells.Anti-inflammatory effects: The polysaccharides found in chaga mushroom, such as beta-glucan, work to reduce inflammation in the body and protect against autoimmune disorders. Betulinic acid also has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce pain and discomfort associated with chronic diseases.Digestive benefits: Chaga mushroom contains various polysaccharides that work to improve digestion by promoting healthy gut bacteria, reducing inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, and protecting against leaky gut syndrome.
Chaga mushroom is a powerful medicinal mushroom that has been used for centuries to treat a variety of health conditions. Its active constituents, including betulinic acid, polysaccharides such as beta-glucan, and various minerals and vitamins, work through several different mechanisms of action to provide relief from autoimmune disorders, improve digestion, and protect against chronic diseases such as cancer. Whether taken as a supplement or incorporated into natural medicines, chaga mushroom is an important fungus to have on hand for its numerous health benefits.
Further Reading on Natural Medicine:
Mushrooms: Cordyceps Lion’s Mane Maitake Shiitake Mushroom
Herbs: Chamomile